By Manish Shirke
AI Systems Architect & DevOps Leader
Exploring the future of intelligent automation
In the evolving landscape of Agentic AI, understanding the distinction between horizontal and vertical agents is essential for designing effective systems.
Horizontal Agents
A horizontal agent is general-purpose and designed to perform a wide range of tasks across multiple domains. It functions like a universal assistant, capable of managing emails, scheduling, ordering food, controlling IoT devices, and more. Horizontal agents require strong memory, contextual awareness, and modular architecture to manage diverse functionalities.
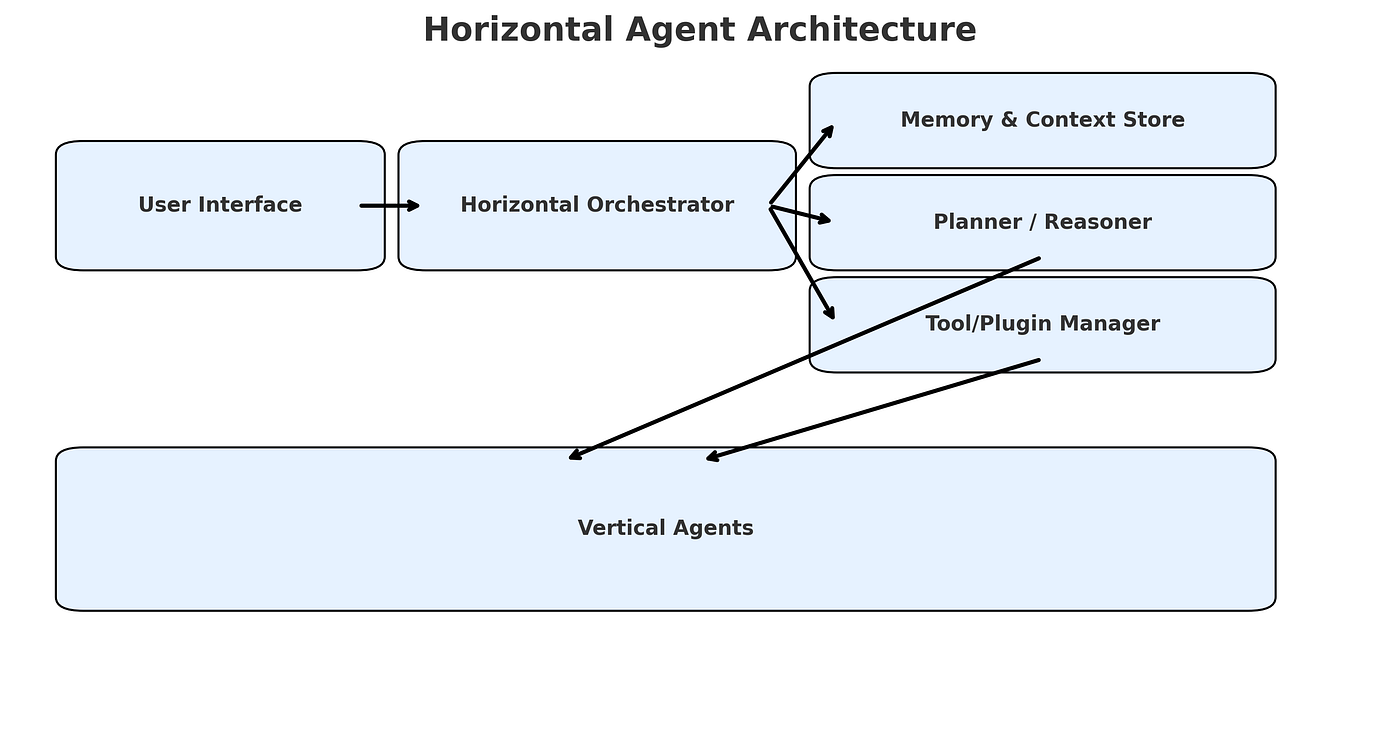
Vertical Agents
Vertical agents, in contrast, are domain-specific. They are deeply integrated into a single application or workflow. These agents are tailored for tasks like Kubernetes troubleshooting, legal document analysis, or customer service in finance. Their narrow focus enables higher reliability and domain expertise.

Comparing Horizontal and Vertical Agentic AI
In practice, powerful Agentic AI systems often combine both types. A horizontal orchestrator delegates tasks to vertical specialists, akin to how a manager coordinates with domain experts. Understanding and leveraging this hierarchy is key to building scalable, efficient, and intelligent agentic systems.
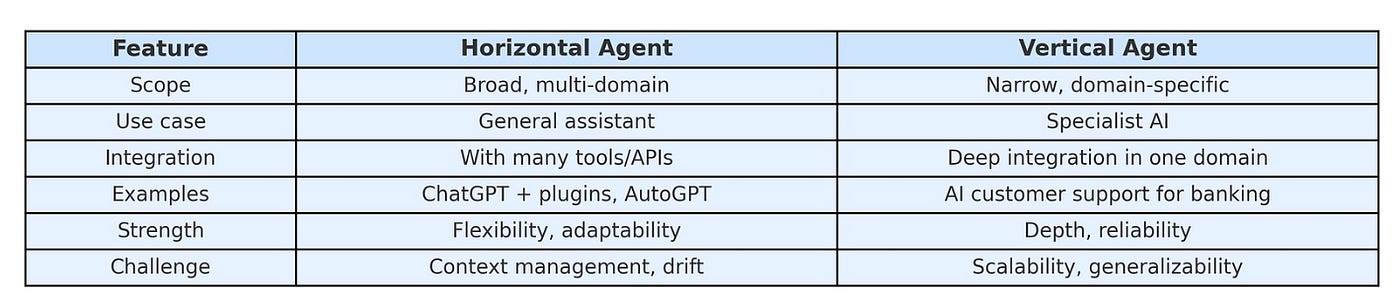
Following table compares Horizontal versus vertical agents:
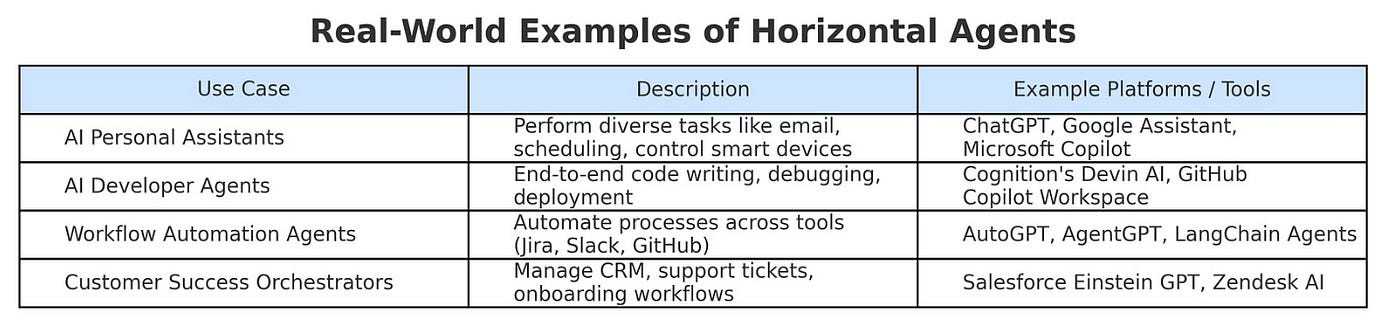
Let us see how Horizontal agents and vertical Agents are being used in real world. Below table shows some real world examples of Horizontal agents.
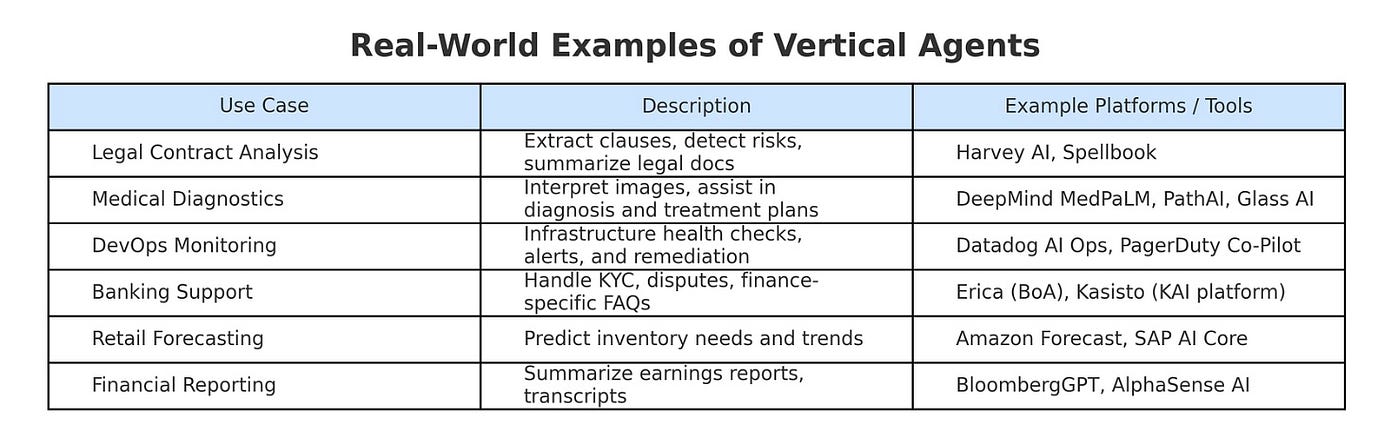
Below table shows some real world examples of Vertical agents.
Conclusion
As AI continues to evolve from passive tools into autonomous agents, understanding the difference between horizontal and vertical agent architectures becomes essential for building effective, scalable systems. Horizontal agents excel in flexibility and orchestration, acting as generalists capable of navigating diverse tasks across domains. In contrast, vertical agents bring depth and specialization, offering domain-specific intelligence embedded within tightly integrated workflows.
Real-world platforms like ChatGPT, AutoGPT, and Devin showcase the power of horizontal orchestration, while specialized systems such as Harvey (legal), Med‑PaLM (medical), PathAI (pathology), and Erica (banking) exemplify how vertical agents are reshaping industry-specific applications.
Looking ahead, the most impactful AI ecosystems will likely combine the strengths of both models: horizontal agents orchestrating and delegating tasks to a federation of vertical experts. This hybrid approach will enable organizations to harness the power of general reasoning alongside domain mastery — driving productivity, personalization, and innovation at scale.

Leave a comment